An ointment is a semisolid topical dosage form intended for application to the skin or mucous membranes to deliver drug locally (e.g., anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antibiotic) or sometimes systemically. Ointments are generally greasy, occlusive, and provide strong emollient action, making them suitable for dry, scaly lesions and for drugs needing prolonged contact time.
Types of ointment bases
- Hydrocarbon (oleaginous) bases: petrolatum, paraffin. Very occlusive, excellent barrier, poor water washability.
- Absorption bases: anhydrous lanolin, hydrophilic petrolatum. Can absorb water and form w/o emulsions.
- Water-removable bases (o/w creams): emulsifying wax, cetostearyl alcohol blends. Less greasy, washable.
- Water-soluble bases: polyethylene glycols (PEGs). Non-greasy, washable, but can dehydrate skin and may be incompatible with some drugs.
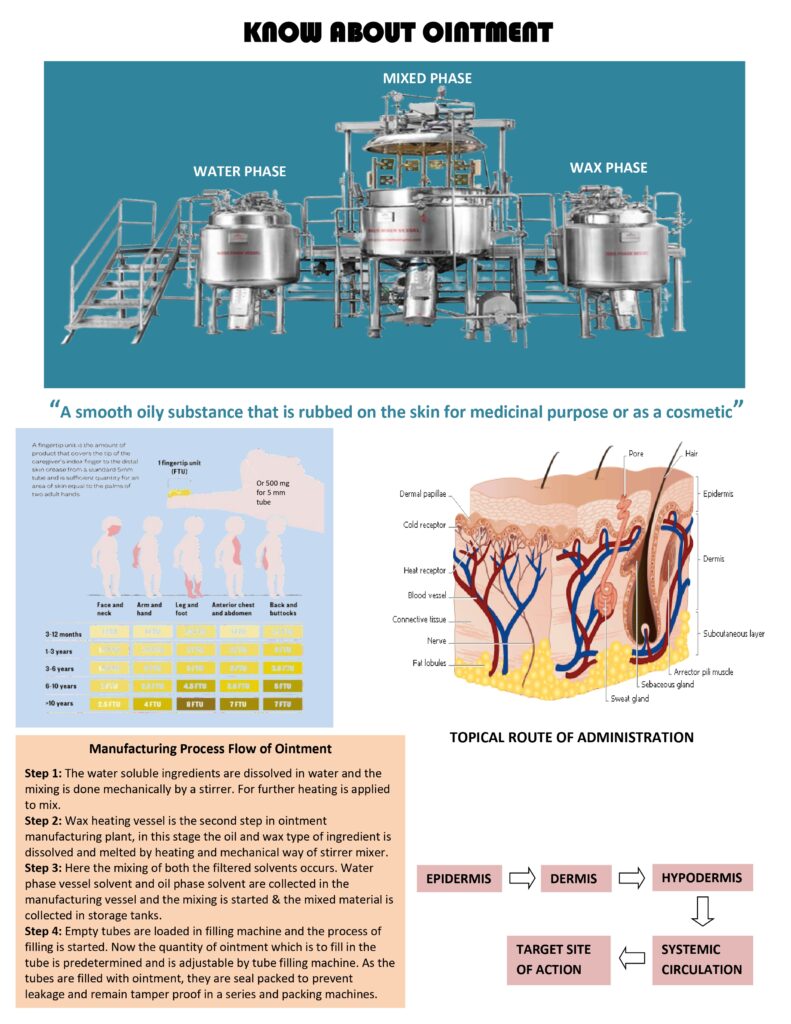
Manufacturing (typical steps)
- Weighing and dispensing of API and excipients with line clearance.
- Melting and mixing: base components melted (if needed) and mixed under controlled temperature to prevent degradation.
- Incorporation of API: either dissolved (for soluble drugs) or levigated with suitable levigating agent to reduce grittiness for insoluble drugs. Uniform dispersion is critical.
- Homogenization to achieve smooth texture and content uniformity; control shear to avoid air entrapment.
- Deaeration (vacuum) to remove trapped air.
- Filling and sealing into tubes/jars under hygienic conditions; crimping and labeling with batch traceability.
Critical quality attributes (CQA) & tests
- Appearance and homogeneity (no phase separation, no grittiness)
- Assay and content uniformity
- Viscosity/rheology (spreadability and patient feel)
- Particle size (for dispersed drugs)
- pH (for emulsified systems)
- Microbial limits and preservative efficacy (where water is present)
- In-vitro release/permeation (as applicable)
- Stability: physical (separation), chemical (potency), and microbial.
GMP controls
Control raw material quality, mixing temperatures/times, cleaning validation, environmental hygiene, and robust in-process checks to ensure consistent, safe, and effective ointment batches.





