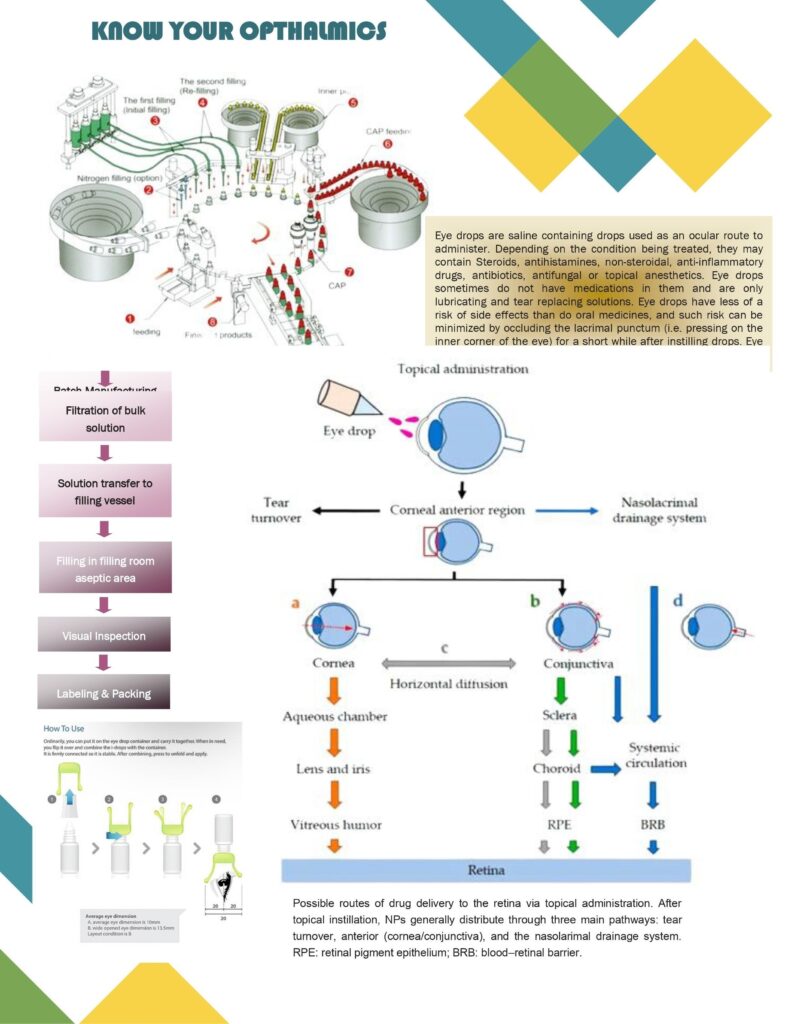
Opthalmics in pharma are dosage forms intended for the eye (topical or intraocular) and therefore demand strict control of sterility, comfort, and safety. Because the eye is highly sensitive, even small deviations in pH, tonicity, particles, or microbial contamination can cause irritation, infection, or damage.
Common ophthalmic dosage forms
- Eye drops (solutions/suspensions/emulsions): most common; require accurate drop size and uniform dose.
- Ointments and gels: longer residence time; blur vision temporarily.
- In-situ gelling systems: liquid transforms into gel in the eye for extended action.
- Intraocular products: highest risk; extremely stringent sterility/endotoxin limits.
Key formulation considerations
- Sterility: mandatory for most ophthalmics; aseptic manufacturing and sterile filtration (where feasible).
- Preservatives: used for multi-dose packs (e.g., benzalkonium chloride), but must be compatible with actives and packaging; avoid or minimize in sensitive patients when possible.
- pH and buffering: typically near physiological (around 7) but balanced with drug stability; avoid strong buffers that irritate.
- Tonicity/osmolality: close to tears to reduce stinging; adjust with salts/sugars.
- Viscosity modifiers: improve contact time (HPMC, CMC, carbomers), but must maintain dropability.
- Suspension quality: controlled particle size, wetting, and resuspendability to ensure uniform dosing.
- Compatibility: container–closure interactions, extractables/leachables, adsorption of drug to plastics, and preservative loss into packaging.
Manufacturing and packaging
- Aseptic processing is common: sterilize bulk (filtration/heat), sterilize components, fill in controlled environments.
- Packaging options: LDPE dropper bottles, BFS containers, single-dose vials, and specialized systems (preservative-free multi-dose pumps).
- Container Closure Integrity (CCI) is critical to maintain sterility throughout shelf life.
Critical quality tests (typical)
- Appearance, assay, impurities, pH, osmolality, viscosity, drop size/delivered dose
- Sterility, endotoxin (as applicable), microbial limits (for non-sterile intermediates)
- Particulate matter/clarity, preservative content and antimicrobial effectiveness (PET/AET)
- Stability including photostability and in-use stability for multi-dose products





