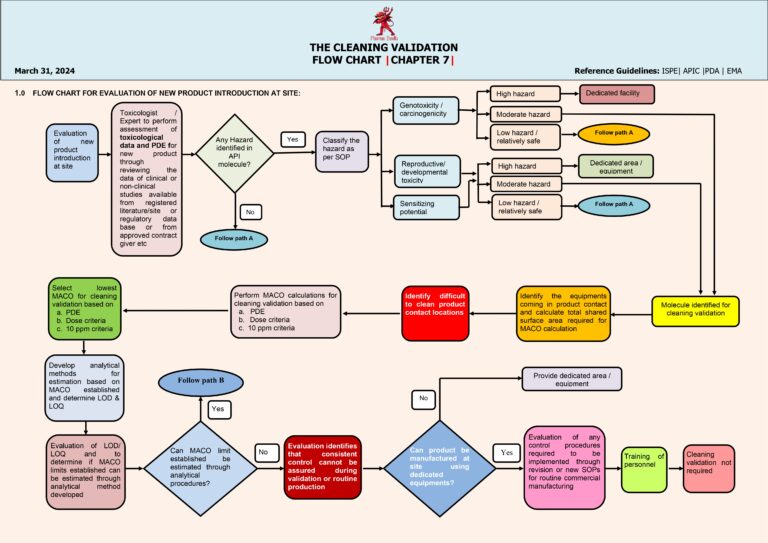
Cleaning Validation (Chapter 8) Worst Case Selection Criteria

Worst-case selection in cleaning validation is a structured, risk-based approach used to choose the most challenging product, equipment, and process conditions to demonstrate that the cleaning procedure is effective for all routine manufacturing scenarios. The goal is to validate one…